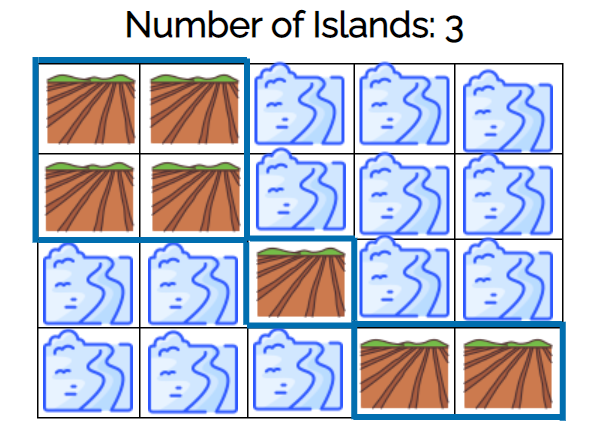
Number of Islands
Level - Medium
Statement:
Given an
m x n2D binary grid which represents a map of'1's (land)and'0's (water), return the number of islands.
An island is surrounded by water and is formed by connecting adjacent lands horizontally or vertically. You may assume all four edges of the grid are all surrounded by water.
Example 1
Input: grid = [
["1","1","0","0","0"],
["1","1","0","0","0"],
["0","0","1","0","0"],
["0","0","0","1","1"]
]
Output: 3
Example 2
Input: grid = [
["1","1"],
["1","0"],
["1","0"],
["0","0"]
]
Output: 1
You can try this at:
Algorithm
- Initialize a queue<int[]> to store the co-ordinates(x,y) of the elements in the grid and a visited array to keep track of the visited elements.
- Loop through all the elements in the grid.
- If the element is 1(land) and has not been visited before, increment the count of islands and perform BFS on that element.
- To perform BFS on an element:
- Initialize the queue with the starting co-ordinate(0,0) and mark it as visited by setting visited[x][y] = true.
- Loop through the following steps until the queue is empty:
- Poll the co-ordinate from the queue.
- Move in all four directions (up, down, left, and right) and if an element in any direction is 1 and has not been visited, put that co-ordinate in the queue and mark it as visited.
- After the BFS is complete, we will have visited all the elements in the island. We will continue to loop through the grid and perform BFS on any unvisited 1(land) elements until we have found all the islands.
- Return the count of islands
Code
- Java
- Python
- CPP
public void bfs(int x,int y,char[][] grid,boolean[][] visited,int n,int m){
Queue<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>();
int[] dx = {0,0,-1,1};
int[] dy = {-1,1,0,0};
// init the queue
q.add(new int[]{x,y});visited[x][y] = true;
while(!q.isEmpty()){
int[] point = q.poll();
// go to all the directions
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
int new_x = dx[i]+point[0],new_y = dy[i]+point[1];
if(new_x>=0 && new_x<n && new_y>=0 && new_y<m && grid[new_x][new_y]=='1' && !visited[new_x][new_y]){
q.add(new int[]{new_x,new_y});
visited[new_x][new_y] = true;
}
}
}
return;
}
public int numIslands(char[][] grid) {
int n = grid.length;
int m = grid[0].length;
// track visited to avoid infinite loop
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[n][m];
int count = 0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<m;j++){
if(grid[i][j]=='1' && !visited[i][j]){
count++;
bfs(i,j,grid,visited,n,m);
}
}
}
return count;
}
from collections import deque
class Solution:
def bfs(self, x, y, grid, visited, n, m):
queue = deque()
dx = [0, 0, -1, 1]
dy = [-1, 1, 0, 0]
# Initialize the queue
queue.append((x, y))
visited[x][y] = True
while queue:
point = queue.popleft()
# Go to all directions
for i in range(4):
new_x = dx[i] + point[0]
new_y = dy[i] + point[1]
if (
0 <= new_x < n
and 0 <= new_y < m
and grid[new_x][new_y] == '1'
and not visited[new_x][new_y]
):
queue.append((new_x, new_y))
visited[new_x][new_y] = True
def numIslands(self, grid):
n = len(grid)
m = len(grid[0])
# Track visited to avoid infinite loop
visited = [[False] * m for _ in range(n)]
count = 0
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
if grid[i][j] == '1' and not visited[i][j]:
count += 1
self.bfs(i, j, grid, visited, n, m)
return count
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
void bfs(int x, int y, vector<vector<char>>& grid, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int n, int m) {
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
vector<int> dx = {0, 0, -1, 1};
vector<int> dy = {-1, 1, 0, 0};
// Initialize the queue
q.push(make_pair(x, y));
visited[x][y] = true;
while (!q.empty()) {
pair<int, int> point = q.front();
q.pop();
// Go to all directions
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int new_x = dx[i] + point.first;
int new_y = dy[i] + point.second;
if (new_x >= 0 && new_x < n && new_y >= 0 && new_y < m && grid[new_x][new_y] == '1' && !visited[new_x][new_y]) {
q.push(make_pair(new_x, new_y));
visited[new_x][new_y] = true;
}
}
}
}
int numIslands(vector<vector<char>>& grid) {
int n = grid.size();
int m = grid[0].size();
// Track visited to avoid infinite loop
vector<vector<bool>> visited(n, vector<bool>(m, false));
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == '1' && !visited[i][j]) {
count++;
bfs(i, j, grid, visited, n, m);
}
}
}
return count;
}
};
Complexity
Time Complexity:
O(N*N))
Space Complexity:
O(N*N)